40 draw and label a cell membrane
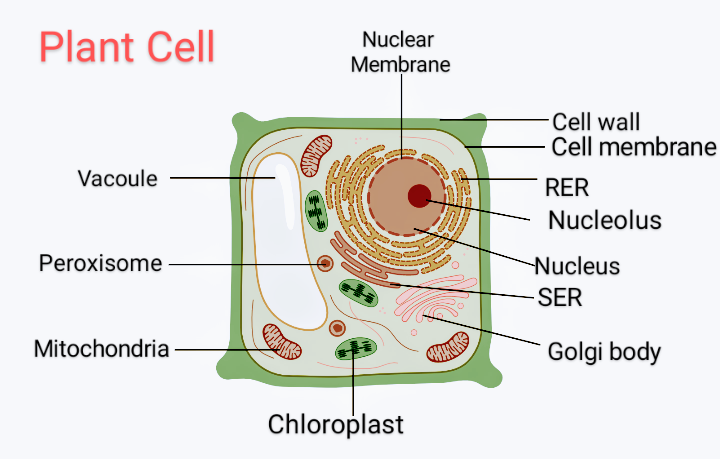
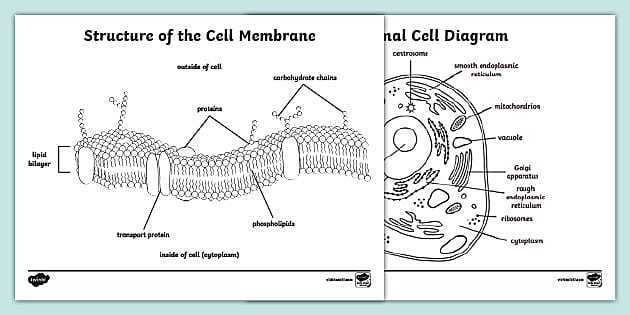
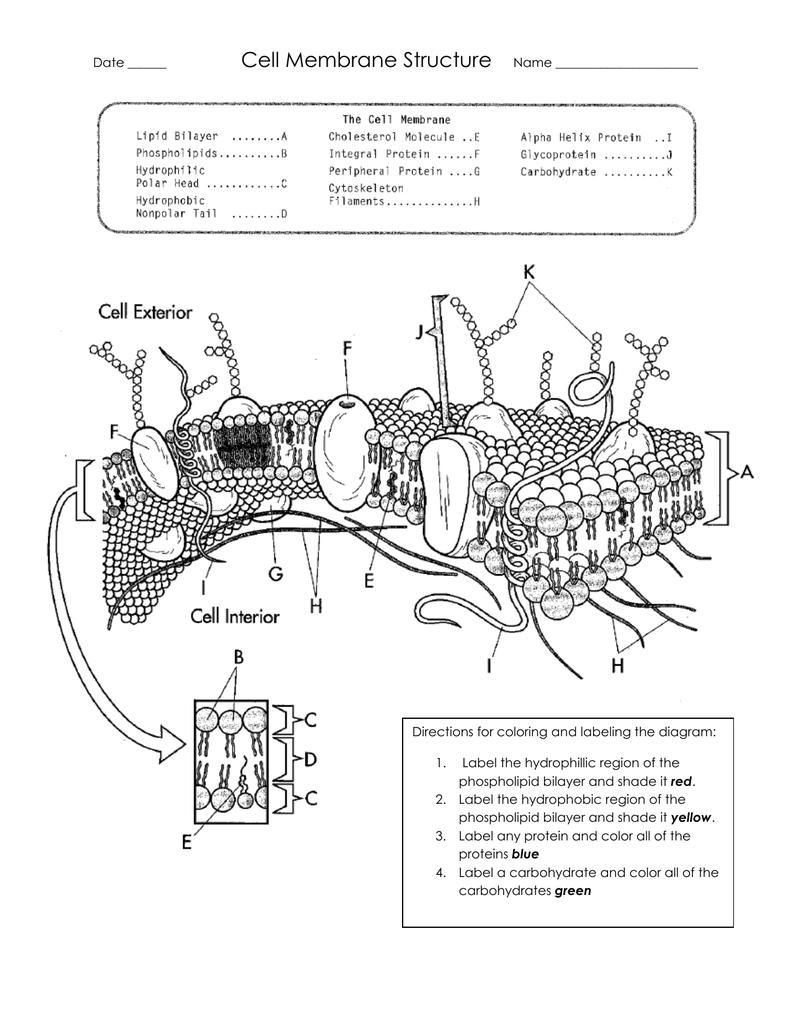
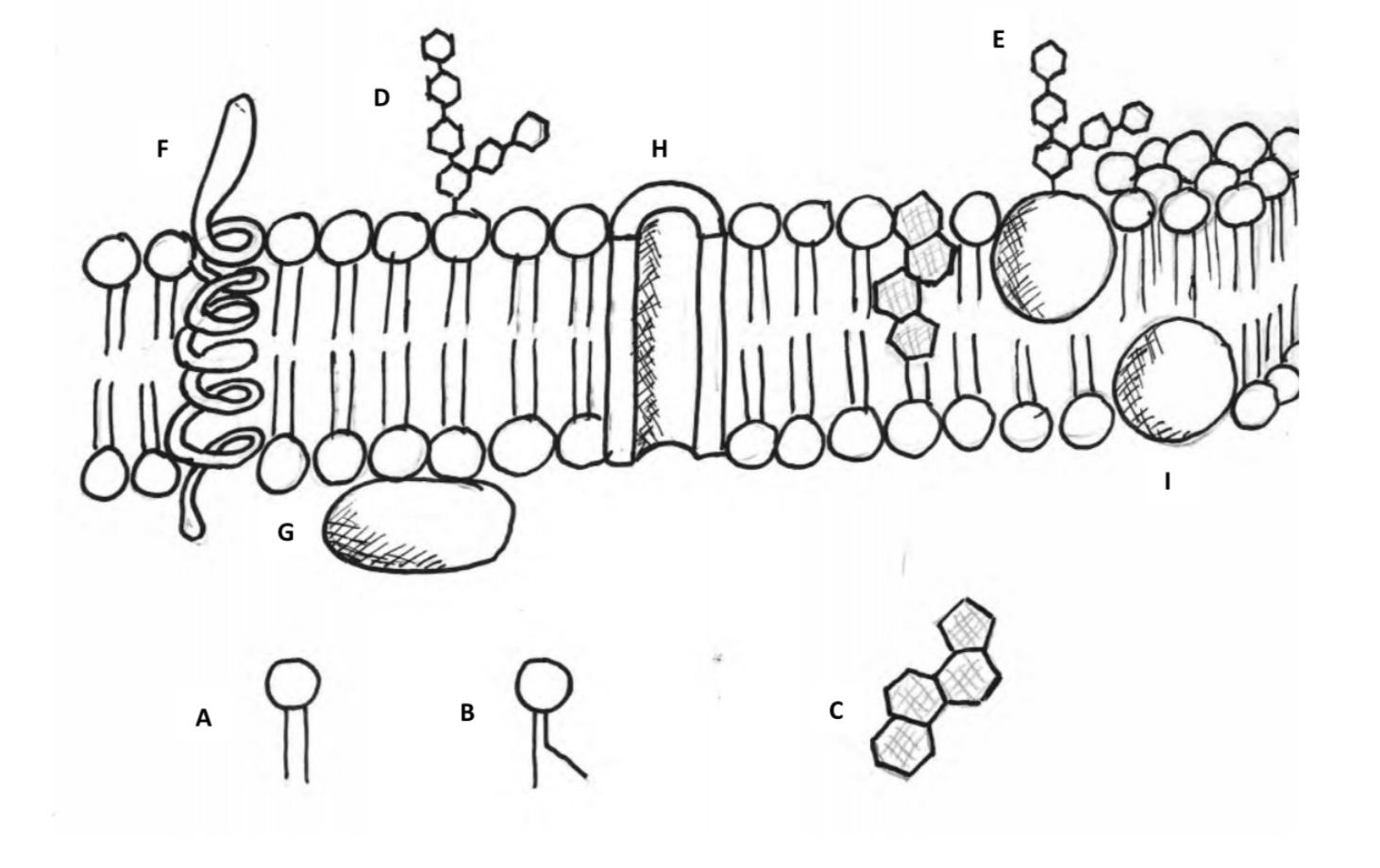
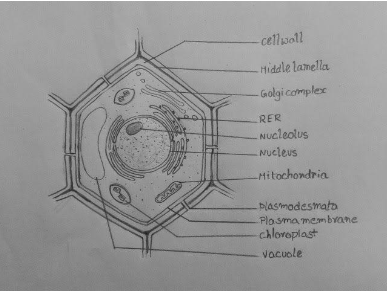
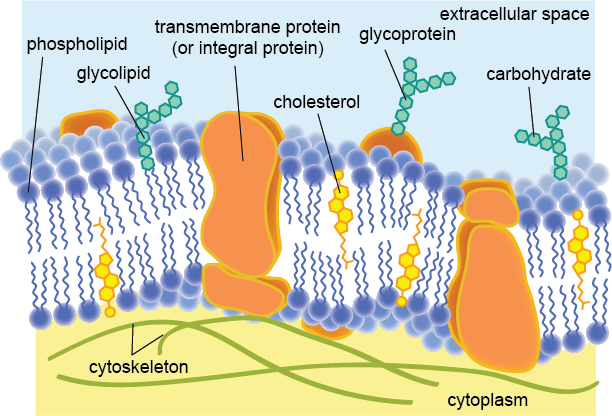
IB Biology Notes - 2.4 Membranes - IB Guides Membranes 2.4.1 Draw and label a diagram to show the structure of membranes.. Figure 2.4.1 - Annotated drawing of a cell membrane. 2.4.2 Explain how the hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties of phospholipids help to maintain the structure of cell membranes.. Phospholipid molecules make up the cell membrane and are hydrophilic (attracted to water) as well as hydrophobic (not attracted to water ... 2.4.1 Draw and label a diagram to show the structure of membranes When drawing and labeling a diagram of the plasma membrane you should be sure to include:The phospholipid bilayer with hydrophobic 'tails' and hydrophilic 'h...
Cell Membrane Function and Structure - ThoughtCo The cell membrane (plasma membrane) is a thin semi-permeable membrane that surrounds the cytoplasm of a cell. Its function is to protect the integrity of the interior of the cell by allowing certain substances into the cell while keeping other substances out. It also serves as a base of attachment for the cytoskeleton in some organisms and the ...
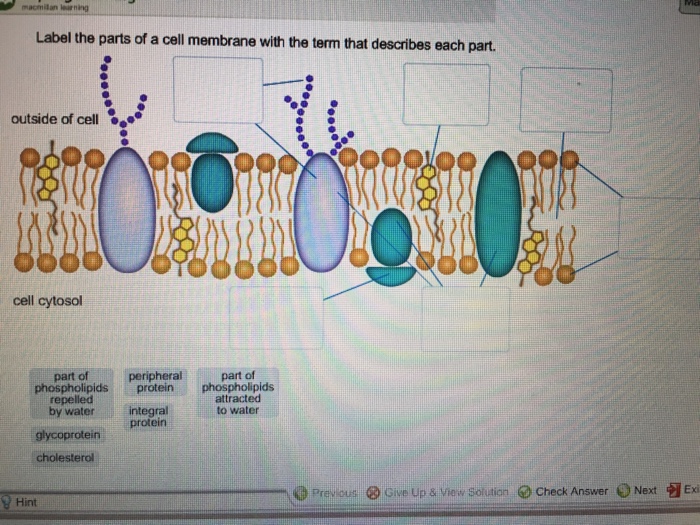
Draw and label a cell membrane
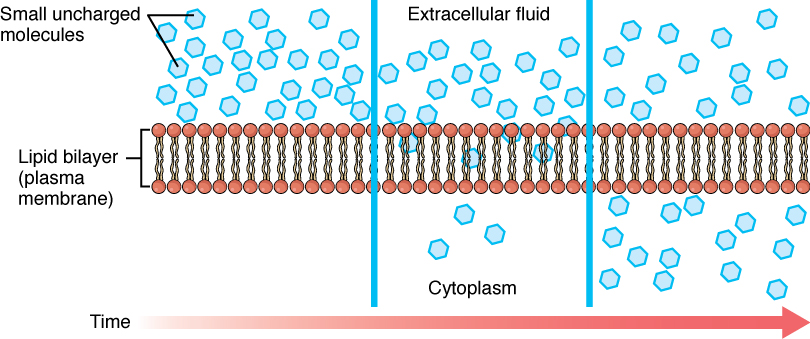
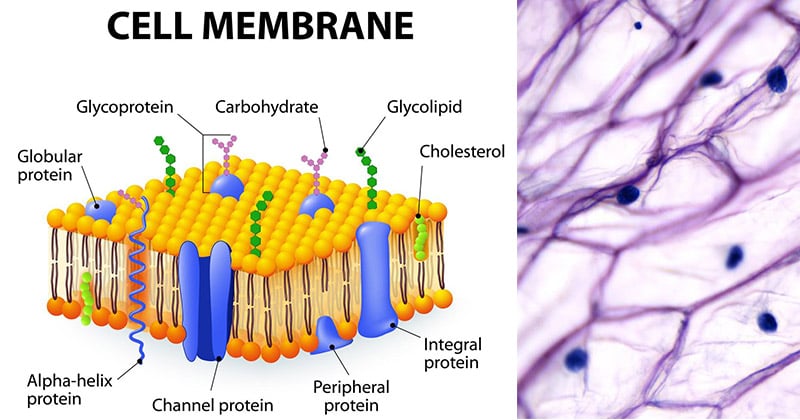
Structure of the plasma membrane (article) | Khan Academy Image modified from OpenStax Biology. The principal components of the plasma membrane are lipids (phospholipids and cholesterol), proteins, and carbohydrate groups that are attached to some of the lipids and proteins. A phospholipid is a lipid made of glycerol, two fatty acid tails, and a phosphate-linked head group. Cell membrane | Definition, Function, & Structure | Britannica The chemical structure of the cell membrane makes it remarkably flexible, the ideal boundary for rapidly growing and dividing cells. Yet the membrane is also a formidable barrier, allowing some dissolved substances, or solutes, to pass while blocking others. Lipid-soluble molecules and some small molecules can permeate the membrane, but the lipid bilayer effectively repels the many large ... Draw a cell in a hypertonic, hypotonic and isotonic solutions.... A hypertonic solution has a higher concentration of solutes than the cell, while a hypotonic solution has a lower concentration of solutes than the cell. An isotonic solution has an equal concentration of solutes to the cell. Let's draw a cell in each of these three tonicity conditions and describe what happens to the cell in each scenario.
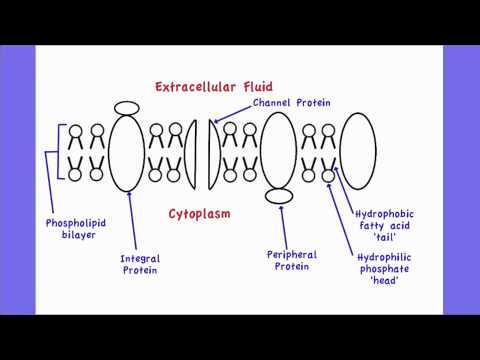
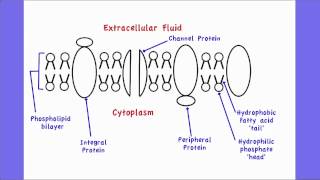
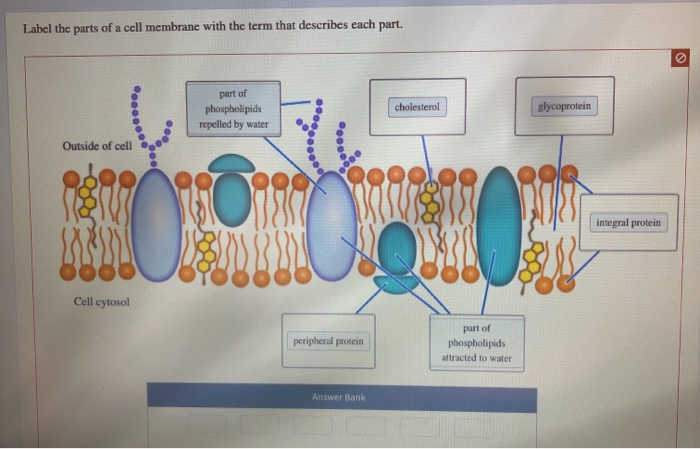
Draw and label a cell membrane. Phospholipid structure (video) | Khan Academy Phospholipids are molecules that form the cell membrane. They consist of a polar phosphate head group and two nonpolar fatty acid tails joined by a glycerol backbone. The phosphate group can link with different molecules, such as serine or choline, to generate diverse kinds of phospholipids. The fatty acid tails can have cis or trans double ... Structure of the Cell Membrane | Biology for Majors I - Lumen Learning A cell's plasma membrane defines the cell, outlines its borders, and determines the nature of its interaction with its environment. Cells exclude some substances, take in others, and excrete still others, all in controlled quantities. The plasma membrane must be very flexible to allow certain cells, such as red and white blood cells, to ... The Cell Membrane | Anatomy and Physiology I - Lumen Learning The lipid bilayer forms the basis of the cell membrane, but it is peppered throughout with various proteins. Two different types of proteins that are commonly associated with the cell membrane are the integral proteins and peripheral protein (Figure 3). As its name suggests, an integral protein is a protein that is embedded in the membrane. Fluid mosaic model: cell membranes article - Khan Academy The purpose of the cell membrane is to hold the different components of the cell together and to protect it from the environment outside the cell. The cell membrane also regulates what enters and exits the cell so that it doesn't lose too many nutrients, or take in too many ions. ... A drawing showing the three main cell membrane components ...
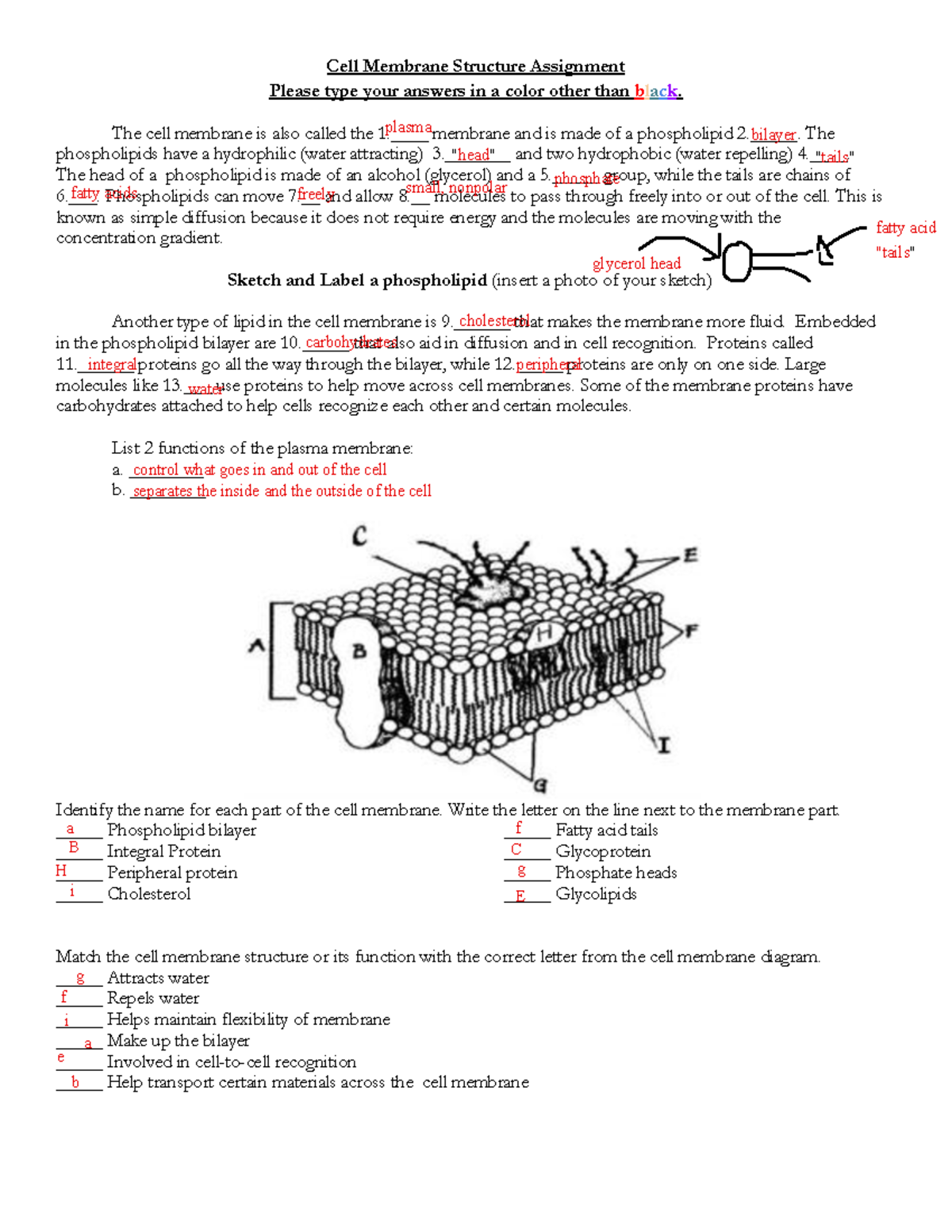
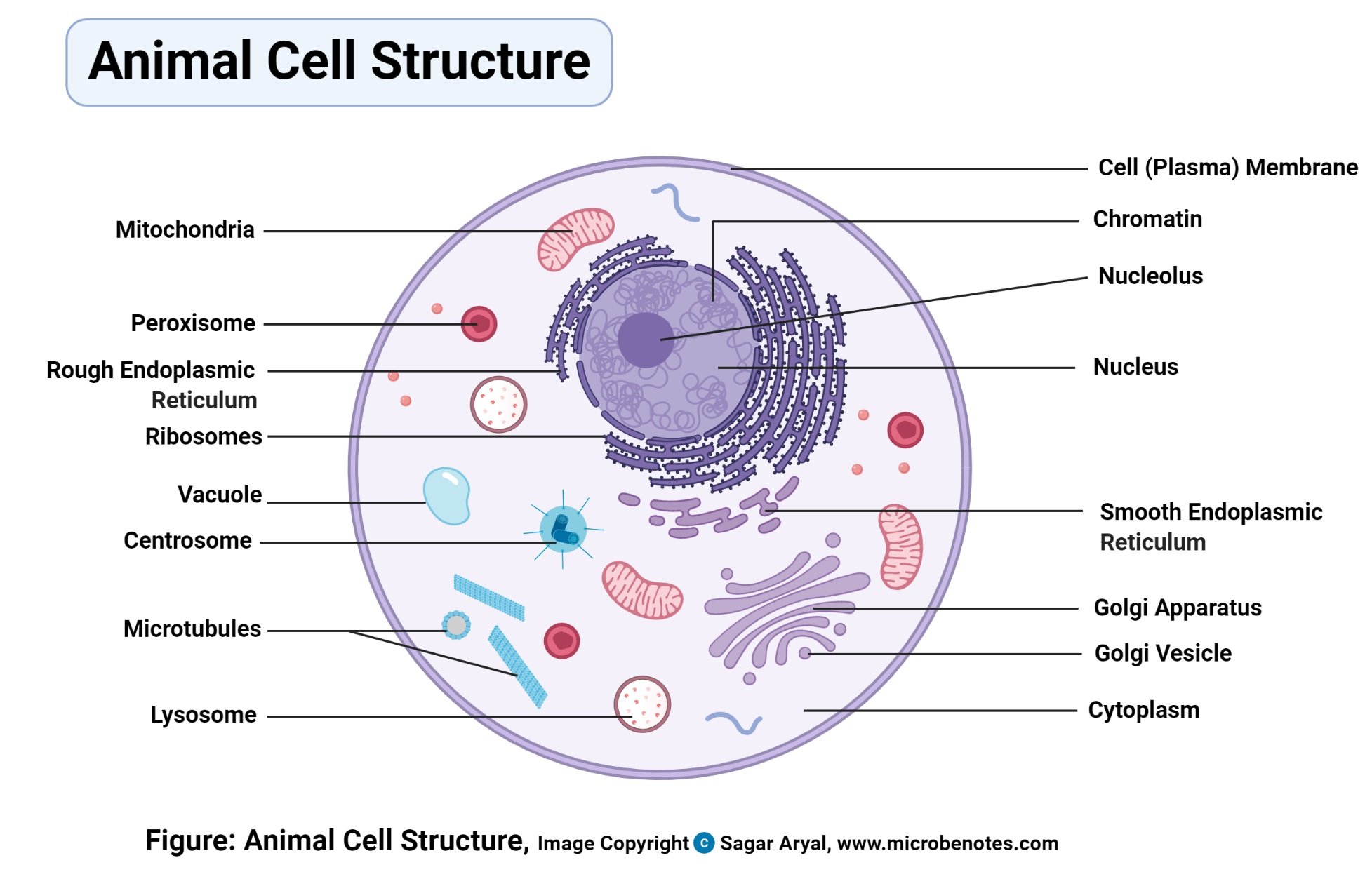
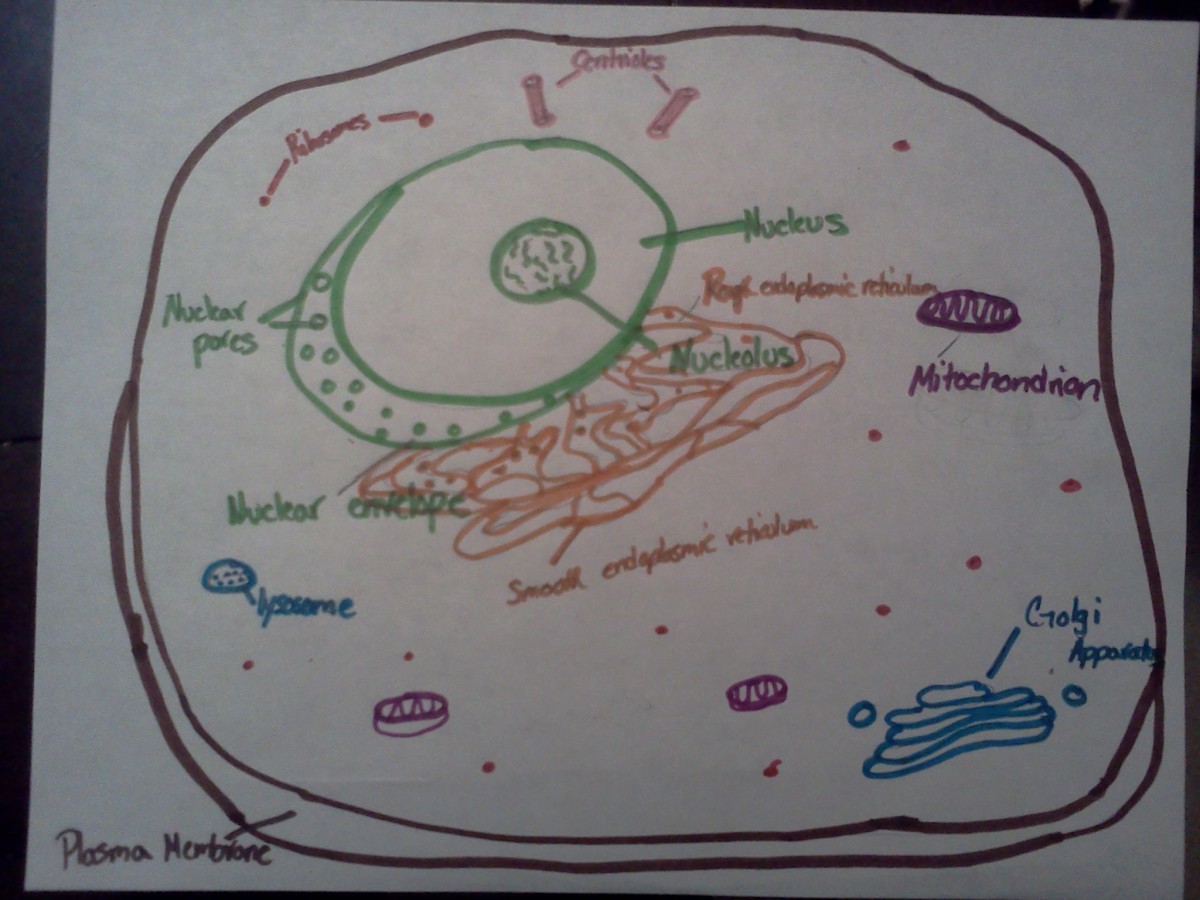
Passive transport and active transport across a cell membrane article ... The cell membrane is one of the great multi-taskers of biology. It provides structure for the cell, protects cytosolic contents from the environment, and allows cells to act as specialized units. A membrane is the cell's interface with the rest of the world - it's gatekeeper, if you will. This phospholipid bilayer determines what molecules ... Plasma membrane and cytoplasm (article) | Khan Academy The plasma membrane—the outer boundary of the cell—is the bag, and the cytoplasm is the goo. Of course, a cell is ever so much more than just a bag of goo. It's a complex, highly organized unit, the basic building block of all living things. And the plasma membrane and cytoplasm are actually pretty sophisticated. CELL MEMBRANE LABEL Diagram | Quizlet Verified answer. biology. A scientist used a pesticide on one field and left a nearby field untreated. Next, she marked off five plots of equal size in each field. Then she dug up a cubic meter of soil beneath each plot and counted the earthworms in the soil. The tables show her data. Cells | Biology I Laboratory Manual - Lumen Learning Draw a starfish egg with a diameter of approximately 2 cm. Label the cell membrane, chromatin, nucleolus, nuclear envelope, nucleus, and cytoplasm. Cheek Epithelial Cells Cells that cover a surface, whether outside the body or inside the body are called epithelial cells.
Labeling a cell membrane Diagram | Quizlet Start studying Labeling a cell membrane. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. ... Cell Transport. 17 terms. iriswang0327 Teacher. Of Mice and Men Chapter 2 Vocabulary. 20 terms. Images. T_Anthony4 Teacher. Vocabulary 2: 20 terms. CLMSGordon Teacher. Diffusion and Osmosis | Biology I Laboratory Manual The cell membrane plays the dual roles of protecting the living cell by acting as a barrier to the outside world, yet at the same time it must allow the passage of food and waste products into and out of the cell for metabolism to proceed. ... Observe the Elodea cells under the compound microscope at high power (400 X) and draw a typical cell ... How to Draw an Animal Cell: 11 Steps (with Pictures) - wikiHow 1. Draw a simple circle or oval for the cell membrane. The cell membrane of an animal cell is not a perfect circle. You can make the circle misshapen or oblong. The important part is that it does not have any sharp edges. [1] Also know that the membrane is not a rigid cell wall like in plant cells. Draw a cell in a hypertonic, hypotonic and isotonic solutions.... A hypertonic solution has a higher concentration of solutes than the cell, while a hypotonic solution has a lower concentration of solutes than the cell. An isotonic solution has an equal concentration of solutes to the cell. Let's draw a cell in each of these three tonicity conditions and describe what happens to the cell in each scenario.
Cell membrane | Definition, Function, & Structure | Britannica The chemical structure of the cell membrane makes it remarkably flexible, the ideal boundary for rapidly growing and dividing cells. Yet the membrane is also a formidable barrier, allowing some dissolved substances, or solutes, to pass while blocking others. Lipid-soluble molecules and some small molecules can permeate the membrane, but the lipid bilayer effectively repels the many large ...
Structure of the plasma membrane (article) | Khan Academy Image modified from OpenStax Biology. The principal components of the plasma membrane are lipids (phospholipids and cholesterol), proteins, and carbohydrate groups that are attached to some of the lipids and proteins. A phospholipid is a lipid made of glycerol, two fatty acid tails, and a phosphate-linked head group.

















Post a Comment for "40 draw and label a cell membrane"